Greater Capybara in South America Leave a comment
What’s Capybara:Capybara is a large rodent native to South America. They are part of the genus Hydrochoerus and are closely related to guinea pigs and rock cavies. They are the largest rodent in the world and can grow to be up to 4 feet long and weigh up to 140 pounds.Capybaras are semi-aquatic animals and can be found near bodies of water such as rivers, ponds, and swamps. They are excellent swimmers and can remain submerged for up to 5 minutes. They have webbed feet and dense fur that helps them to stay buoyant in the water.Capybaras are herbivores and their diet consists mainly of grasses and aquatic plants. They are also known to eat fruits and vegetables. They are active during the day and can be found grazing in groups.Capybaras are social animals and live in groups of up to 100 individuals. They have a complex social hierarchy and communicate with each other through vocalizations such as barks, whistles, and purrs.Capybaras are considered a near threatened species due to habitat loss and hunting. They are also sometimes hunted for their meat and pelts. In some areas they are protected by law, but in others they are considered a pest and hunted.Capybaras are also known to be very friendly and docile animals, making them popular exotic pets. However, owning one as a pet is illegal in some states, and it is important to research the laws and regulations before owning one.In conclusion, Capybaras are large, semi-aquatic rodents native to South America, known for their friendly and docile nature, complex social hierarchy, and their diet of grasses and aquatic plants. They are near threatened species and hunted for their meat and pelts. Owning one as a pet is illegal in some states.
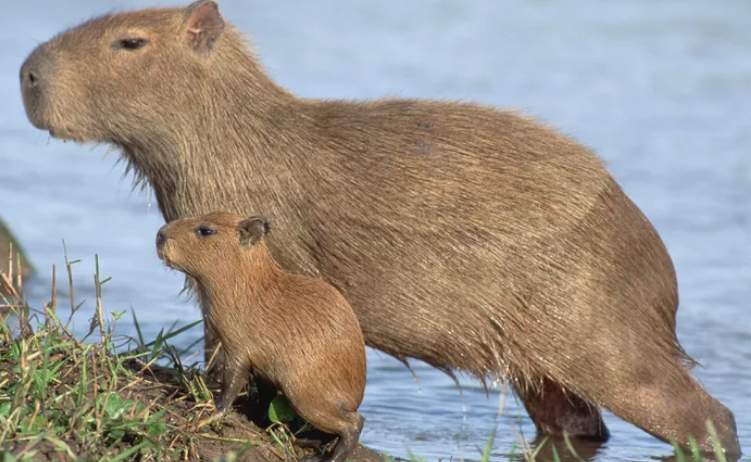

Greater Capybara in South America
The Greater Capybara, also known as the capybara or hydrochoerus hydrochaeris, is a large rodent native to South America. These animals are found in a variety of habitats, including grasslands, savannas, and wetlands, and are known for their friendly and social nature.
One of the most distinctive features of the capybara is its size. They can grow up to 4 feet long and weigh up to 140 pounds, making them the largest rodent in the world. They have short, dark brown fur that is dense and waterproof, which helps them stay buoyant in water. Their bodies are barrel-shaped and their heads are broad and flat. They have small ears, small eyes, and large teeth that are constantly growing.
Capybaras are herbivores and feed primarily on grasses, aquatic plants, and fruits. They spend most of their time in or near water, and are excellent swimmers. They can remain submerged for up to five minutes and can swim at speeds of up to 6 miles per hour. They are also known to use their webbed feet to walk on the bottom of rivers and lakes to find food.
One of the most interesting things about capybaras is their social behavior. They live in groups of up to 100 individuals and have a complex system of communication. They use a variety of vocalizations, including barks, whistles, and purrs, to communicate with each other. They also use scent marking to communicate with other members of their group.
Capybaras are also known for their friendly nature towards humans. They are not aggressive and are often kept as pets in South America and other parts of the world. They are also used as a source of food and as a hunting target.
Despite their large size, capybaras have relatively few natural predators. Jaguars, crocodiles, and anacondas are among the animals that prey on capybaras, but these predators are not common in most of the capybaras’ range.
Capybaras are not considered a threatened species, but their populations have been impacted by hunting and habitat loss. They are protected by law in some countries, but illegal hunting still occurs in many parts of their range.
In conclusion, the Greater Capybara, also known as the capybara or hydrochoerus hydrochaeris, is a large rodent native to South America. They are known for their friendly and social nature, their herbivorous diet, their excellent swimming abilities and their large size. Despite their friendly nature towards humans, their populations have been impacted by hunting and habitat loss. Efforts should be made to protect these animals and their habitats to ensure their survival in the wild.
See also:Great Eared Nightjar in USA
How to Identify Capybara?
Capybaras (Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris) are large, herbivorous rodents that are native to South America. They are the largest rodents in the world and are known for their friendly and docile nature. Capybaras are typically found in wetlands and near bodies of water, such as rivers and lakes.
Physical Characteristics:
- Body: Capybaras have a barrel-shaped body that is covered in short, dense fur. Their fur is usually brown or dark brown in color, but can also be reddish or yellowish.
- Head: Capybaras have a large, round head with small ears that are set close to the head. They have small eyes and a short, broad nose.
- Teeth: Capybaras have large, sharp teeth that are constantly growing. They use their teeth to gnaw on tough vegetation.
- Tail: Capybaras have a short, thick tail that is covered in fur.
- Size: Adult capybaras can weigh up to 140 pounds and can be up to 4 feet long, including their tail.
Behavior:
- Social: Capybaras are social animals and live in groups of up to 100 individuals. They communicate with each other through a variety of vocalizations, including barks, whistles, and purrs.
- Feeding: Capybaras are herbivores and primarily eat grasses, aquatic plants, and fruits. They are known to be good swimmers and will often submerge themselves in water to escape predators or to find food.
- Sleep: Capybaras are active during the day and night, but they do take naps throughout the day.
Habitat:
- Range: Capybaras are found in South America, primarily in Brazil, Venezuela, Colombia, and parts of Ecuador, Paraguay, Peru, Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, and Trinidad and Tobago.
- Habitat: Capybaras are found in a variety of habitats, including wetlands, grasslands, and forests. They are most commonly found near bodies of water, such as rivers, lakes, and swamps.
Similar species:
- Nutria: Nutria are also large, aquatic rodents that are found in South America. They have a similar body shape to capybaras, but are smaller and have a longer tail. Nutria also have webbed hind feet and a thicker, coarser coat of fur.
- Muskrat: Muskrats are also aquatic rodents that are found in North America. They are smaller than capybaras and have a more elongated body shape. Muskrats also have a thicker, coarser coat of fur and a longer, thinner tail.
How to Identify a Capybara in the wild:
- Observe the animal’s size and shape. Capybaras are the largest rodents in the world, and have a barrel-shaped body that is covered in short, dense fur.
- Look for the animal’s head. Capybaras have a large, round head with small ears that are set close to the head. They have small eyes and a short, broad nose.
- Observe the animal’s behavior. Capybaras are typically found near bodies of water, such as rivers and lakes, and are known to be good swimmers. They are also social animals and live in groups.
- Note the animal’s habitat. Capybaras are native to South America, primarily in Brazil, Venezuela, Colombia, and parts of Ecuador, Paraguay, Peru, Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, and Trinidad and Tob.
Why Do Capybaras Take Yuzu Baths?
Capybaras, also known as Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris, are the largest rodents in the world, native to South America. They are found in a wide range of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and wetlands. Capybaras are semi-aquatic animals and they spend a lot of time in and around water, so it’s no surprise that they enjoy taking baths.
Taking a bath is not only a way for capybaras to clean themselves but also a way for them to relax and have fun. The warm water helps to soothe their muscles and reduce stress, and the yuzu fruit and leaves that are often used in their baths have a relaxing scent that is believed to be beneficial for their skin and overall well-being.
Yuzu is a type of citrus fruit that is native to East Asia, it’s similar to a grapefruit but with a sweeter taste and a more fragrant aroma. The fruit and leaves of the yuzu plant are rich in antioxidants, vitamin C, and other nutrients that are beneficial for the skin. The scent of yuzu is also said to have a relaxing effect on the body and mind, making it a perfect addition to a capybara’s bath.
Capybaras are also known to be very social animals. They live in groups and often spend time grooming each other, playing, and cuddling. Taking a yuzu bath together can be a bonding experience for them, and it’s a way for them to strengthen their social connections within the group.
It’s not just capybaras that enjoy yuzu baths, people also use yuzu bath products such as yuzu bath salts, yuzu body wash, yuzu soap and so on, as a way to relax and rejuvenate the skin. It’s believed that the antioxidants, vitamin C and other nutrients in yuzu can help to improve the skin’s elasticity and firmness, while also reducing inflammation and redness.
In conclusion, capybaras take yuzu baths as a way to clean themselves, relax, and bond with other capybaras. The warm water and the scent of yuzu help to soothe their muscles and reduce stress while the fruit and leaves are believed to be beneficial for the skin. It’s not just capybaras that enjoy yuzu baths, people can also benefit from the relaxing and rejuvenating properties of this unique citrus fruit.
Should You Keep a Capybara as a Pet?
Capybaras are large, semi-aquatic rodents native to South America. They can make great pets for the right person, but they are not suitable for everyone. Before deciding to keep a capybara as a pet, it is important to consider the specific needs of these animals and whether you are able to meet them.
One of the most important things to consider when keeping a capybara as a pet is their size. Adult capybaras can reach up to 4 feet in length and weigh up to 140 pounds. This means they require a lot of space, both indoors and outdoors. They need a large enclosure with a pool or pond for swimming, as well as a grassy area for grazing. They also need a secure, fenced area for exercise and exploration.
Capybaras are also very social animals and do best when kept in pairs or groups. Keeping a single capybara as a pet can lead to loneliness and behavioral issues. If you are considering keeping a capybara as a pet, it is important to have the time, energy, and resources to provide for multiple animals.
Another important consideration when keeping a capybara as a pet is their dietary needs. Capybaras are herbivores and require a diet of grasses and other vegetation. They also need access to fresh water at all times. In captivity, a diet of hay, fresh vegetables and fruits, and specially formulated capybara pellets can be provided.
Capybaras also have specific health needs. They are prone to certain health issues, such as dental problems and foot infections, and require regular veterinary checkups. They also need regular grooming to keep their coat in good condition.
In terms of behavior, Capybaras are generally docile and friendly animals, but they can be skittish and nervous around unfamiliar people and animals. They can be trained to do simple tricks and be leash-trained. They do well in households with children and other pets, but proper introductions and socialization are required.
In summary, capybaras can make great pets for the right person, but they are not suitable for everyone. They require a lot of space, both indoors and outdoors, and are best kept in pairs or groups. They also have specific dietary and health needs that must be met. It is important to carefully consider all of these factors before deciding to keep a capybara as a pet.
See also:Capybara on Wikipedia
Capybara Animal Facts?
Capybaras, also known as “water rats,” are large, semi-aquatic rodents that are native to South America. They are the largest rodent in the world and can grow up to 4 feet in length and weigh up to 140 pounds. Their dense, dark brown fur helps them to blend in with their natural environment, making them difficult to spot in the wild.
Capybaras are found throughout much of South America, including in Venezuela, Colombia, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay, and Argentina. They live near water sources, such as rivers, lakes, and swamps, and are excellent swimmers. They can remain submerged for up to five minutes and can even sleep while floating in the water.
Capybaras are herbivores and their diet consists mainly of grasses and aquatic plants. They also eat fruits, vegetables, and grains if they are available. They are known to graze for several hours a day, and they can consume up to 8 pounds of vegetation daily. They are also able to obtain water through the plants they eat.
Capybaras are social animals and live in groups of 10-100 individuals. These groups are led by a dominant male, known as the alpha, and are made up of females and their young. The group is very cohesive and the individuals communicate with each other through a variety of vocalizations, including barks, whistles, and purrs.
Capybaras have a number of unique adaptations that help them to survive in their aquatic habitat. They have webbed feet and dense fur that helps to keep them buoyant in the water. They also have sharp incisors that are constantly growing, which they use to chew on vegetation. Their eyes, ears, and nostrils are all located on the top of their head, which allows them to see, hear, and smell potential predators while remaining mostly submerged in the water.
Capybaras reproduce year-round, with peak breeding occurring during the rainy season. Females give birth to litters of 2-8 young, known as capybaritas, after a gestation period of 130-150 days. The young are born fully furred and are able to swim within hours of birth. They are weaned at around three months of age and reach sexual maturity at around 18 months.
Capybaras have few natural predators in the wild. Their main predators are large cats, such as jaguars and pumas, and crocodiles. They are also hunted by humans for their meat and fur. In addition to these threats, capybaras are also affected by habitat loss and fragmentation.
In recent years, capybaras have become increasingly popular as pets. They are relatively easy to care for and have friendly and docile personalities. However, it is important to remember that they are large animals that require a lot of space and have specific dietary and health needs. Before getting a capybara as a pet, it is important to carefully research their care requirements and to make sure that you have the resources to provide for them.
In addition to being kept as pets, capybaras also play an important role in the ecosystem as a keystone species. They help to control the growth of aquatic plants and their grazing helps to maintain the balance of wetland ecosystems. They also provide food for a variety of predators and their droppings serve as a source of nutrients for plants.
In conclusion, capybaras are fascinating and unique animals that play an important role in the ecosystem. They are herbivores that live near water sources, are excellent swimmers, and live in groups. They have a number of adaptations that help them to survive in their aquatic habitat.